GitLab
This page describes GitLab, which is a software for Git repository management and software development that can run on your own server. GitLab also offers a hosted online service at https://gitlab.com.
Overview
GitLab is Open Source and offers Git repository management, code reviews, issue tracking, activity feeds and wikis.
Features
Major GitLab features are depicted in this article on techdo.me.
Some highlights:
- User management.
- SSH key management for accessing a repo via SSH and mapping to GUI user.
- Repository/project permissions (private, protected or public). Users and groups.
- View commits.
- Comments.
- Issue tracking.
- Markdown support.
- Branches and tags can be created in GUI.
- Merge requests. Code review.
- New files can be created and in the GUI.
- Files can be edited in the GUI.
- A wiki per project (in separate Git repo).
- Notifications.
- Visualization of commits, branches, etc.
- 18 GitLab features are moving to open source (März 2020)
- Web IDE
Planning
- Issues (tickets) can only be created on project level. Issue are passed from bottom to down (project -> subgroup -> group). The higher the level, the more issues are gathered and shown in issue boards.
- Epics can only be created on subgroup and group level. Epics are passed from bottom to down (subgroup -> group). The higher the level, the more epics are gathered and shown in epic list/board and roadmaps.
- Roadmaps are based on epics (after dates are given). Roadmaps are passed and enriched from bottom to down (subgroup -> group).
- Permissions (members) are inherited and passed from top to bottom (group -> subgroup -> project). A permission granted on group level cannot be removed on subgroup or project level. Therefore, if we need to split permissions (e.g. for product and customer train), subgroups are needed.
- Each group can contain multiple subgroups and each subgroup can contain multiple projects.
- Group, subgroup and project names can be changed easily without impact on references. But paths (in URL) shall remain stable in order to keep references (merge requests, commits, links) valid. Therefore, paths shall be generic (e.g. team1, team2, ...) and short.
Access to repositories
The GitLab GUI always shows the links you need to use for accessing (cloning) the Git repositories either via HTTP or SSH.
Example URLs for project/repository:
HTTP access:
http://gitlab.example.com/group1/project1.git
SSH access on port 22:
git@gitlab.example.com/group1/project1.git
- Note: The repo must be addressed with a absolute path (do not use ":" between hostname and pathname)
The corresponding clone commands are:
git clone http://gitlab.example.com/group1/project1.git git clone ssh://git@gitlab.example.com/group1/project1.git
Notes:
- For HTTP you need to authenticate with your GitLab user credentials, if it's not a public repo.
- It's recommended using SSH for accessing the repositories with a Git client.
- The SSH connect must go directly to the host GitLab has been installed on (no proxy in between).
- For SSH you need to always login as user git. The user mapping will be made via your SSH key(s).
- For SSH you need to authenticate with a SSH private key matching the public key you need to register in your GitLab user profile.
- The SSH keys must be unique. You can't add a public key to multiple user profiles. The keys are added to ~git/.ssh/authorized_keys.
- For SSH you need to take care using the correct SSH key, e.g. just add following to ~/.ssh/config:
Host gitlab.example.com IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_emptypass StrictHostKeyChecking no UserKnownHostsFile /dev/null
- For SSH you can check the general SSH access and authentication by just connecting to the server with a native SSH client. In addition, your GitLab user mapping will be responded by the server as e.g. Welcome to GitLab, Peter Pan!. A successful connect (using SSH port forwarding) looks like:
> ssh git@gitlab.example.com
X11 forwarding request failed on channel 0
PTY allocation request failed on channel 0
Welcome to GitLab, Peter Pan!
Connection to gitlab.example.com closed.
Operations
See Operations for info about installing and maintaining GitLab.
Docker
See hub.docker.com for running GitLab as Docker container.
Creating the container:
docker run --detach \
--hostname gitlab.example.com \
--publish 9443:9443 --publish 9080:9080 --publish 9022:22 \
--name gitlab \
--restart always \
--volume /srv/gitlab/config:/etc/gitlab \
--volume /srv/gitlab/logs:/var/log/gitlab \
--volume /srv/gitlab/data:/var/opt/gitlab \
gitlab/gitlab-ce:latest
GitLab configuration gitlab.rb:
external_url 'https://gitlab.example.com:9443'
nginx['ssl_certificate']= "/etc/gitlab/ssl/fullchain.pem"
nginx['ssl_certificate_key'] = "/etc/gitlab/ssl/privkey.pem"
gitlab_rails['gitlab_shell_ssh_port'] = 9022
gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_from'] = 'gitlab@example.com'
gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_display_name'] = 'GitLab example.com'
gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_reply_to'] = 'gitlab@example.com'
gitlab_rails['smtp_enable'] = true
gitlab_rails['smtp_address'] = "mail.example.com"
gitlab_rails['smtp_port'] = 587
gitlab_rails['smtp_user_name'] = "user"
gitlab_rails['smtp_password'] = "pass"
gitlab_rails['smtp_domain'] = "mail.example.com"
gitlab_rails['smtp_authentication'] = "plain"
gitlab_rails['smtp_enable_starttls_auto'] = true
Notes about running GitLab on a Docker host with Port 80, 443 and 22 already occupied:
- GitLab must be configured to set the external ports like 9443 and/or 9080. Once you set "external_url 'https://gitlab.example.com:9443'", nginx will listen on port 9443.
- Setting the SSH port
gitlab_rails['gitlab_shell_ssh_port'] = 9022
- does only work when the port forwarding from Docker is e.g. 9022->22. 9022->9022 did not work for me.
- All these HTTP/HTTPS and SSH configured are used as ports in the GitLab user interface, e.g. in the clone URL.
- You can/should create virtual webservers on the Docker host serving port 443 and 80 and redirecting both the the external GitLab URL.
- For TLS with Let's Encrypt see TLS.
Update:
docker stop gitlab docker rm gitlab docker pull gitlab/gitlab-ce:latest docker run ...
Troubleshooting:
docker logs gitlab docker exec -it gitlab bash
Ports:
Weblinks:
TLS
- https://about.gitlab.com/2016/04/11/tutorial-securing-your-gitlab-pages-with-tls-and-letsencrypt/
- https://webnugget.de/setting-up-gitlab-with-free-ssl-certs-from-lets-encrypt-on-ubuntu-14-04/
- https://gitlab.com/gitlab-com/blog-posts/issues/24
Help
The GitLab GUI has an excellent online help available at
http://gitlab.example.com/help
Agile Project/Product Management
- How to set up GitLab groups and projects to run multiple Agile teams with microservices
- Getting started with GitLab: Mastering project management
- Custom workflow statuses for issues and tasks - introduced in version 18.2 (July 2025)
Issues
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/issues/
- Issue Templates
- Defined within .gitlab/issue_templates/
- Exmaple for a "Bug" template Bug.md:
# Details
# Customer information
* Client reported the bug:
# Workflow
Please mark the checks if the corresponding step is __finished__.
- [ ] Bug can be reproduced :frame_photo:
- [ ] Shipment :cruise_ship:
- [ ] Yes, the feature can be shipped automatically (continuous delivery)
- [ ] No, we need to align date of shipment
- [ ] Approved :vertical_traffic_light:
## Additional information
* Effort Estimation (in PT): _please add estimated duration using a [quick action](https://gitlab.kruedewagen.de:9443/help/user/project/quick_actions)_
* Is a date of shipment communicated to the client (yes|no)?
- If yes, which date:
/label ~"bug"
- Story Points per Weight (nur ab Starter)
- Time Tracking
- Crosslinking Issues
#xxx https://gitlab.com/<username>/<projectname>/issues/<xxx>
Issue Boards
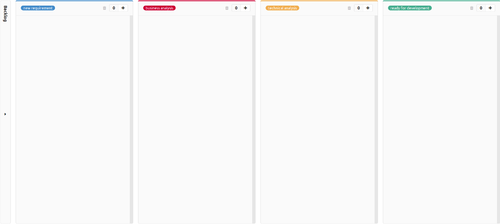
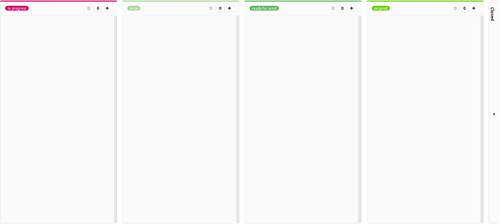
Issue boards are controlled by labels. Board can be created by project/repo and also on group level.
A feature board respective product backlog with a workflow for requirement engineering could look like:
- backlog
- new requirement
- business analysis
- technical analysis
- ready for development
- in progress
- in qa
- ready for production
- on production
- closed
This feature boards looks like following:
EPICs
- Seamless top-down and bottoms-up planning with epics and roadmap
- 3 Major improvements to epics in GitLab 12.7
- "Move epic to other group" feature introduced in version x.y
- Some "assign epic" features introduced in GitLab 18.2
User Story
See also
Operations
Alerts und Incidents
- Designing Incident Management from scratch
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/operations/incident_management/
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/operations/incident_management/generic_alerts.html
- Downtime happens, but GitLab Incident Management can help
- Alerts werden per Schnittstelle erzeugt
- Beispiel
TIMESTAMP=$(date +%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S%z)
FINGERPRINT=$(date +%s)
curl --request POST \
--data '{"title": "Test Alert", "description": "Short description of the alert", "start_time": "'$TIMESTAMP'", "service": "My little service", "monitoring_tool": "Icinga", "hosts": "server", "severity": "medium", "fingerprint": "'$FINGERPRINT'"}' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer <key>" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
https://gitlab.example.com/group1/project1/alerts/notify.json
- Achtung: "fingerprint" muss unique sein, sonst wird kein neuer Alert/Issue erzeugt (z.B. als UUID um wiederkehrende Alert erkennen, Anzahl "Events" wird sonst hochgezählt). "key" wird aus den GitLab-Einstellungen für den Aufruf der Schnittstelle übernommen.
- Incidents können automatisch aus Alerts erzeugt werden (Einstellungen, Template möglich) oder manuell aus einem Alert in der GitLab GUI erstellt werden.
- Incidents sind eine bestimmte Art von Issues mit anderen Detail-Infos (z.B. Severity).
- Incidents haben einen Tag "incident"
Logging
- https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/logs.html
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/logs/#override-default-log-level
- gitlab.rb (hat kaum Effekt)
gitlab_rails['env'] = {
"GITLAB_LOG_LEVEL" => "WARN",
}
registry['log_level'] = 'warn'
gitlab_shell['log_level'] = 'WARN'
gitaly['configuration'] = {
logging: {
level: "warn"
}
}
- Environment variable (Docker)
-e GITLAB_LOG_LEVEL='warn'
Docker Registry
- Aufräumen:
gitlab-ctl registry-garbage-collect
Apps
GitLab Pages
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/pages/introduction.html
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/pages/index.html#getting-started
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/pages/
- https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-pages
- https://gitlab.com/pages?page=1
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/pages/getting_started/pages_from_scratch.html
- https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2016/06/17/ssg-overview-gitlab-pages-part-3-examples-ci/
- https://how-to-stuff.gitlab.io/gitlab-pages-how-to/
- heise+ | Projektdokumentation mit Git leicht gemacht
- https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2025/03/03/build-a-new-website-in-a-few-easy-steps-with-gitlab-pages Build a new website in a few easy steps with GitLab Pages]
In combination with other tools (e.g. markdown converter, CMS):
- See project import tamples in GitLab
- https://www.reddit.com/r/gitlab/comments/870mgo/is_it_possible_to_create_a_gitlab_page_from/
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/development/documentation/styleguide/
- https://www.r-bloggers.com/2020/09/rendering-an-r-markdown-presentation-to-gitlab-pages/
- https://github.com/showdownjs/showdown
- https://getpublii.com/docs/host-static-website-gitlab-pages.html
- How to choose the right static site generator (gitlab.com)
- MkDocs - Project documentation with Markdown.
- https://www.mkdocs.org/
- https://gitlab.com/pages/mkdocs
- Publishing Obsidian.md notes with GitLab Pages (mit MkDocs zur Umwandlung von Markdown in static website)
- https://gitlab.com/pages/hugo
- VitePress
Troubleshooting
- https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/pages/#troubleshooting
- https://forum.gitlab.com/t/gitlab-ce-docker-gitlab-pages-fails-after-upgrade-to-14-0/54756
- Logs
gitlab-ctl tail gitlab-pages
GitLab Wiki
Move / Migrate / Import a GitLab wiki
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54401112/gitlab-wiki-how-to-import-wiki-when-importing-a-repository
- If you have a mix of master/main: https://www.git-tower.com/learn/git/faq/git-rename-master-to-main
- Delete Wiki: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4922104/is-it-possible-to-completely-empty-a-remote-git-repository
Integrations
Mattermost
OpenProject
Literature and Tutorials
- GitLab Cookbook
- c't 13/16 S.134
- Video Tutorial: Idea to Production on Google Container Engine (GKE)
- Continuous Integration (CI) mit Docker und GitLab: siehe LM 01/18 S.58
- GitLab CI/CD: siehe c't 25/17 S.88
- GitLab 11.0: Auto-DevOps-Feature für alle Nutzer
- GitLab automatisiert die Integration von Kubernetes
- Simple Kubernetes management with GitLab (gitlab.com)
- Continuous Integration: GitLab-CI-Setup: (Ansible und Vagrant) siehe iX 08/18 S.102
- GitLab für DevOps-Teams: siehe LM 04/19 S.22
- GitLab CI und CD installieren und konfigurieren: siehe iX 04/19 S.118
- How to make small changes using GitLab’s Web IDE
- GitLab Product Development Flow: Validation backlog, Problem validation, Design, Solution Validation
- Minimal Viable Change (MVC)
- GitLab als DevOps Toolchain: siehe iX 06/20 S.56, http://ix.de/zy83
- How to use GitLab for DevOps, version control, and more
- 10 tips to make you a productive GitLab user (quick actions)
- Visual Studio code editor: Eight tips for using GitLab VS Code
- Four new tools for your Visual Studio Code and GitLab tool belt
- Einstieg in Git: Eigenen Gitlab-Server mit Docker aufsetzen | heise online
- Top ten GitLab hacks for all stages of the DevOps Platform
- The role of Value Stream Analytics in GitLab's DevOps Platform
- Breaking down CI/CD complexity with parent-child and multi-project pipelines
- How to protect GitLab-connected SSH key with Yubikey
- Parameterizing GitLab CI/CD? (icinga.com Blog)
- How we boosted WebAuthn adoption from 20 percent to 93 percent in two days
- A Short Overview: GitLab Tokens
- Tutorial: How to set up your first GitLab CI/CD component (Python Script)
- Ultimate guide to CI/CD: Fundamentals to advanced implementation
- The ultimate guide to token management at GitLab
- Secure and safe login and commits with GitLab + Yubico
- SAFe without silos in GitLab
- Getting Started with GitLab: Understanding CI/CD
- GitLab: Wiederverwendbare CI/CD-Pipelines erstellen | heise online
- Getting started with GitLab: Working with CI/CD variables
Tools
- RequestBin
- Testen von HTTP Requests, z.B. für den Empfang von Webhooks bei Git/GitLab.
- Siehe "GitLab Cookbook" S.113 - Using webhooks.
- RequestBin gives you a URL that will collect requests made to it and let you inspect them in a human-friendly way. Use RequestBin to see what your HTTP client is sending or to inspect and debug webhook requests.
- Postman
- REST Client, Testen von APIs
- Chrome Browser Extension
- Sendet HTTP Request zu einem Server, auch mit Parameter/Value Variablen von simulierten Formularen
- Siehe "GitLab Cookbook" S.121 - Managing your projects via the API.
GitLab Instanzen und Plattformen
Shortkeys
- "." öffnet Web IDE im jeweiligen Kontext
Weblinks
GitLab official sites:
- GitLab Homepage
- GitLab Community Forum, see also this blog post.
- Chatroom on Gitter
- GitLab Community Edition
- GitLab Community Edition Documentation
- GitLab upcoming releases | GitLab
- Installation
- GitLab Community Edition Update
- GitLab Architecture Overview
- GitLab repository on GitLab
- GitLab repository on GitHub
- GitLab Flow
- GitLab upcoming releases
- GitLab Product Principles
- GitLab First Look - Research program for invites to usability tests, user interviews, surveys, etc.
Communities:
Additional components:
Webcasts:
Other resources:
- Installing GitLab in your local network or your own PC and setting it up to work perfectly, with a guide to change SMTP settings
- Archlinux Wiki
- https://blog.netways.de/2012/06/29/web-oberflache-fur-git-gefallig/
- https://github.com/gitlabhq/gitlab-public-wiki/wiki/Comparison-to-other-Git-web-interfaces
- GitLab as an Alternative Development Platform for Github.com (LinuxCon Europe 2014)
Using under openSUSE:
- https://gist.github.com/rriemann/5163741
- https://gist.github.com/jniltinho/5565606
- https://github.com/n3rdbeere/Installation-guide-for-GitLab6-on-SLES11/blob/master/README.md
- http://www.badzilla.co.uk/openSUSE-12-3-Installation-of-GitLab-Nginx-Apache-and-Drupal-PHP
Markdown:
Continuous Integration (CI/CD):
- GitLab Continuous Integration & Deployment
- GitLab CI Quick Start
- Jenkins Integration
- JIRA Integration
- Seamlessly migrate from Jira to GitLab with Jira2Lab at scale
- Continuous Integration of GitLab-Hosted Docker Projects with Quay.io (gitlab.com)
- GitLab Continuous Integration (pro-linux.de)
- Getting started with GitLab CI/CD and Google Cloud Platform (GitLab)
- Continuous Integration für PHP Anwendungen mit GitLab, Video
- Using GitLab CI/CD for smart home configuration management
- Demo: GitLab + Jira + Jenkins
- Jenkins to GitLab: The ultimate guide to modernizing your CI/CD environment
- How to use GitLab and Ansible to create infrastructure as code
- A quick guide to GitLab CI/CD pipelines
- How to use GitLab for Agile, CI/CD, GitOps, and more
- GitLab’s continuous delivery
- How to use GitLab CI to deploy to multiple environments
- How to harden your self-managed GitLab instance
- Top 10 GitLab workflow hacks you need to know
- How to deploy a PHP app using GitLab's Cloud Run integration
- From code to production: A guide to continuous deployment with GitLab
- Deploy a server using Go with GitLab + Google Cloud
Serverless / FaaS:
- https://about.gitlab.com/2018/12/11/introducing-gitlab-serverless/
- https://entwickler.de/online/agile/gitlab-serverless-angekuendigt-natives-faas-fuer-gitlab-579871325.html
Cloud / GitOps:
- How to deploy to any cloud using GitLab for GitOps
- GitOps with GitLab: How to tackle secrets management
- Best practices to keep secrets out of GitLab repositories
- The ultimate guide to GitOps with GitLab
Release Strategy:
Agile Software Development:
- How to use GitLab for Agile software development (i.e. Issue Board = Product Backlog, Milestone = Sprint, etc.)
- Why GitLab is the right design collaboration tool for the entire team
- Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) with GitLab
Structure and hierachies:
- Best practices to set up organizational hierachies that scale, project -> subgroup -> group, issues, epics, milestones, permissions
Planning:
- How to use GitLab for Agile portfolio planning and project management
- 5 reasons to simplify your agile planning tool configuration with GitLab
- First look: The new Agile planning experience in GitLab
- Unveiling a new epic experience for improved Agile planning
- How to harmonize Agile sprints with product roadmaps
Cloud-Deployment:
Automation:
Compliance:
Documentation:
- Five fast facts about docs as code at GitLab (gitlab.com)
Suche:
Wettbewerb:
Knowledge Graph (GKG):
Comparisons
